Honesty – Integrity Score
The ETC Honesty Score – is a compilation of elements that we call “Checkpoints” that récord the body and verbal reactions of a person when is interviewed and through a detailed observation can be detected if they lie. ETC Honesty Score – The interview is the combination of science, technology, and personal observation to figure out who is lying!
Based on microexpressions, blink and attention rates, signs, clues, reactions, indexes. Critical success factors to identify patterns in the interview (video). The unique combination of science and the art of observation with intuition generates excellent results. (ChP – Checkpoint).
The primary evaluation process is sessions with the potential Candidate/Employee. It is critical to establish rapport and a relaxed atmosphere in the first part of the interview to record Emotions, Blink & Attention rates, used as a baseline/ benchmark.
To fine-tune a proper evaluation for each Statement, you need to study and sometimes check the Video Interview and use facts, hard data, and your Intuition to generate an Honesty Score and conclusions.
Disclaimer: The Honesty Score is not infallible and therefore is a relative value to determine whether the person tells the truth or not based on a scale.

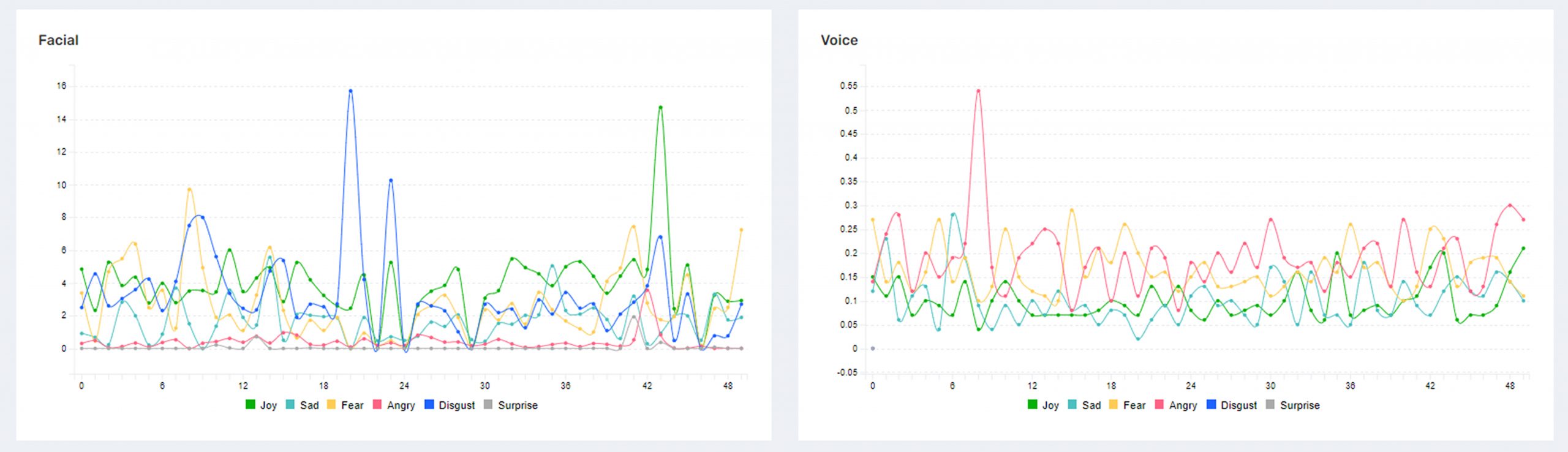
1. Conflicting “Emotions” suggest Lying
Microexpressions flash on a person ́s face for a fraction of a second and show us real emotions.
ETC Solutions video recognition technology, record, and check every 4/100 ́s of a second, micro-expressions and extract emotions at the Question Level.
People telling the truth aligned their thoughts and emotions — individuals lying express distress in their micro-expressions such as Anger, Disgust & Fear.
ETC Method: Evaluate Emotions and related metrics such as P/N, Danger Alert, and TRUST f, in the Interpretation module at the Question and Sessions level you can find trends and patterns that can signal deception.
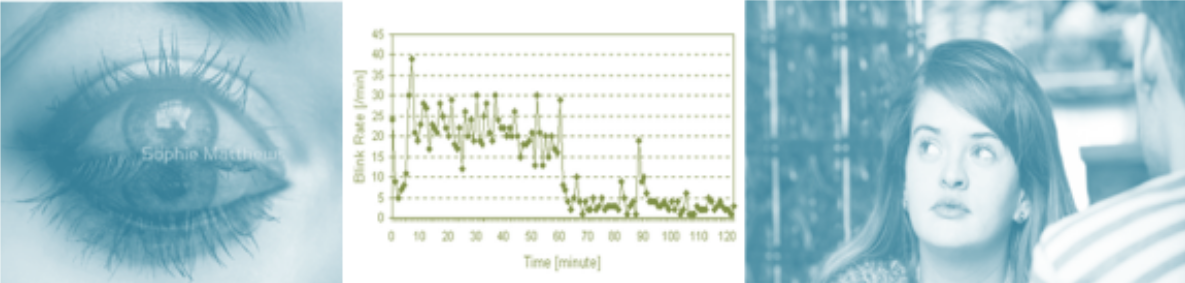

2. Blinking & Attention Rates is a sign of Lying
Normal blink rate: between 6 to 8 times per minute and eyes remain closed each time for one 40th of a second. (one 40th of a second)
When you lie you use more energy because your brain is creating a new reality – A high Blink rate is a common sign of lying.
They blink less than average during the lie period and then have a flurry up to eight times faster than usual afterward.
Key Performance Indicator: Compare Blink Rate in “Soft versus Hard Questions”
Blinking – Signs of Lying (ChP)
Attention rate: Eyes and head movements detect Deception
Avoid looking at you in the Eyes – Not Interested in what is said.
Trained liars know it and will look directly into your eyes.
The reason for No-Eye contact is that they are hiding something.

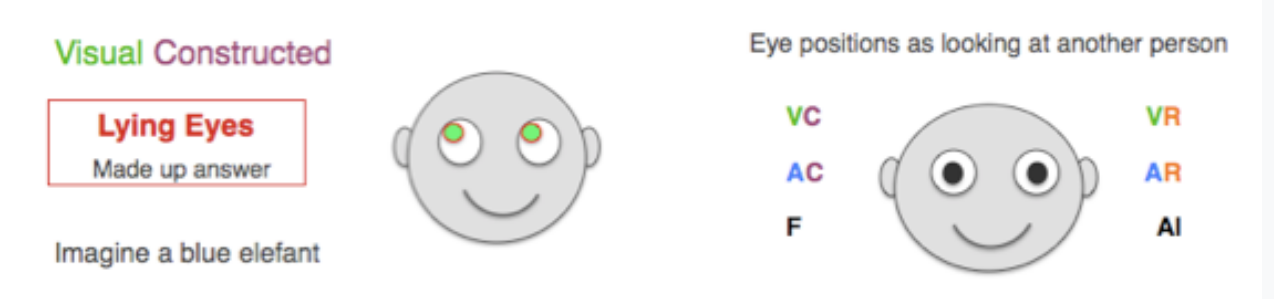
3. Eyes Movements detect Deception.
Eyes Direction for Right-handed people (ChP)
When you tell the truth, you use your memory (right)
When you lie you use your imagination (left – UP)
Closing your eyes more than a second when lying (ChP)

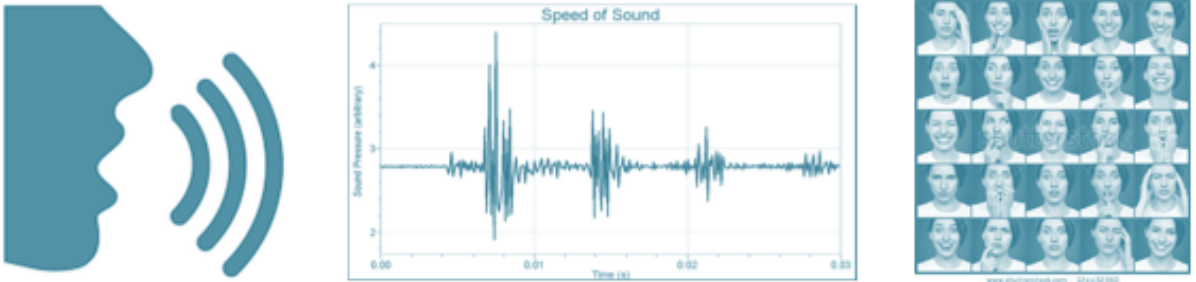
4. Person Voice and talking
Compare the voice’s normal tone and power to:
Talking Speed – Normal (ChP)
Talk Faster or slower than average speed.
Voice Force (ChP)
Tension by lying may result in a higher power.
Higher-Pitched or Quavering Tone (ChP)
Above the normal voice range, tone, and pitch.
Impulsive Emotional Responses “IER” (ChP)
Recognizing the time and duration of response tends to be off.
Delivered aimed not to respond to a question (ChP)
Technically telling the truth, but avoiding answering the question.


5. Verbal Responses (Timing, Duration, Emotions)
Exaggerated Details (ChP)
Provide too much information and details, telling too much!
Pay close attention to reactions/answers to questions (ChP)
A person telling the truth doesn´t feel the need to defend himself.
Stalling Tactics – Asking for a question to be repeated.
Using “Basically or What happened was….”
Confrontational style such as “It depends on what you mean….”
Using “to be honest”, “frankly”, “to be truthful”
Complements from the subject in question.
Invoking Religion – I swear to god. I didn´t.
Selective Memory – Not that I recall.
Ask backward – “Reverse Order Narrative” – Coherence (ChP)
Ask to tell the story in forwarding and backward chronological order.
The person repeats sentences (ChP)
Not ready to reveal much else and keeps repeating.
Mid-sentence jumps and subtle delay to responses (ChP)
Stop in the middle of a sentence, restart, and fail to finish.
Not Using “I” and avoid Contractions (ChP)
Use “did not” instead of “didn´t”
Use of Humor and/or Sarcasm to distract (ChP)
A common practice to avoid the subject


6. Body Language (Face & Head)
Nose Touching (ChP)
Be careful of a “normal” itch that is satisfied with rubbing.
Mouth Covering / Fingers in the Mouth (ChP)
An intuitive gesture that appears in the Mouth.
Eye Rub (ChP)
Is a natural attempt to block words.
Neck Scratch (ChP)
The person is saying “I am not sure I agree.”
Change Head position quickly (ChP)
A mismatch between body language and what is said.
Watch Person Throat “Close up” – (ChP)
Difficult by swallowing saliva and clearing their throat.
Lips Licking (ChP)
A clear sign of insecure gestures.


7. Body Language (Reactions)
Sweating – is a good indication of Lying (ChP)
Impossible to control along with trembling, and blushing.
Person Nods – Incongruence (ChP)
The Head is nodding or shaking in opposition to what is being said.
It´s important so please observe the Person’s Throat again! (ChP)
Difficult by swallowing saliva and clearing their throat.
Fast Breathing (ChP)
Short breaths followed by one deep breath – Dry Mouth.
They tend to point a lot (ChP)
A clear sign of the desire to take the focus off the individual.
Change head position quickly (ChP)
The mismatch between body language and what is said.
Sudden Coughing (ChP)
Start Coughing at a critical moment.


8. Body Language (Positioning & Movements)
They Stand very Still (ChP)
Trying to demonstrate security, you usually are relaxed.
Fidgeting is a result of nervous energy (ChP)
With their own body or random objects.
Breaking Mirroring as a sign of rapport (ChP)
Tend to lean backward a sign of breaking the conversation.
Instinctively cover vulnerable body parts (ChP)
Throat, neck, head, or abdomen. Shrink in on them.
Lowering or hiding the Thumbs (ChP)
A natural and clear sign of lying.
Legs & Hands (ChP)
Palms open, equal to truth, legs, and hands tight means deception.


9. Interrogation Process
Be Careful – You can Misread Deception (ChP)
A stressed person can be mistaken for a liar.
Track Person overall Stress (ChP)
It takes a lot of negative physical/mental energy to maintain a lie.
Repeat the Story (ChP)
Ask to repeat the story multiple times and discover variations.
Use Silence to evaluate signs (ChP)
It´s hard for a liar to avoid filling the silence.
Avoid aggressive interrogation (ChP)
Applying physical & emotional discomfort could create Anxiety.
Never use: Did you…, I know that you…, Why are you lying to me?


10. Evaluate the Person’s Trends & Patterns and Act!
History of Lying (ChP)
Learning to lie is a natural process in child development and will be improved with age.
Lying Patterns (ChP)
Lies come in all shapes and sizes. Evaluate falsehood effects.
People that believe their lies (ChP)
Is there a History and Motive to Lie? – Pathological Liers.
Do you consider the person a Master Lier? (ChP)
After training, people can be very efficient at Lying.
A Master Lier uses a lot of brainpower to manage contradictory information (Truth & Lie) and perfect skills.
Show your evidence and wait for the reaction! (ChP)
If lying continues, it is time to bring the evidence.
Explain that there is a Trust issue! (ChP)
You have to tell the person that you don´t believe anymore.

People lie for various reasons, and the motivation behind lying can differ depending on the individual and the specific situation. Here are some common reasons why people lie:
Self-protection: People may lie to avoid punishment, negative consequences, or harm to themselves. They may fear the consequences of telling the truth and believe that lying will provide them with a better outcome.
